ILLINOIS - CORONARY CTA PRIOR-AUTHORIZATION INFORMATIONAL GUIDE
Updated October 6th, 2016
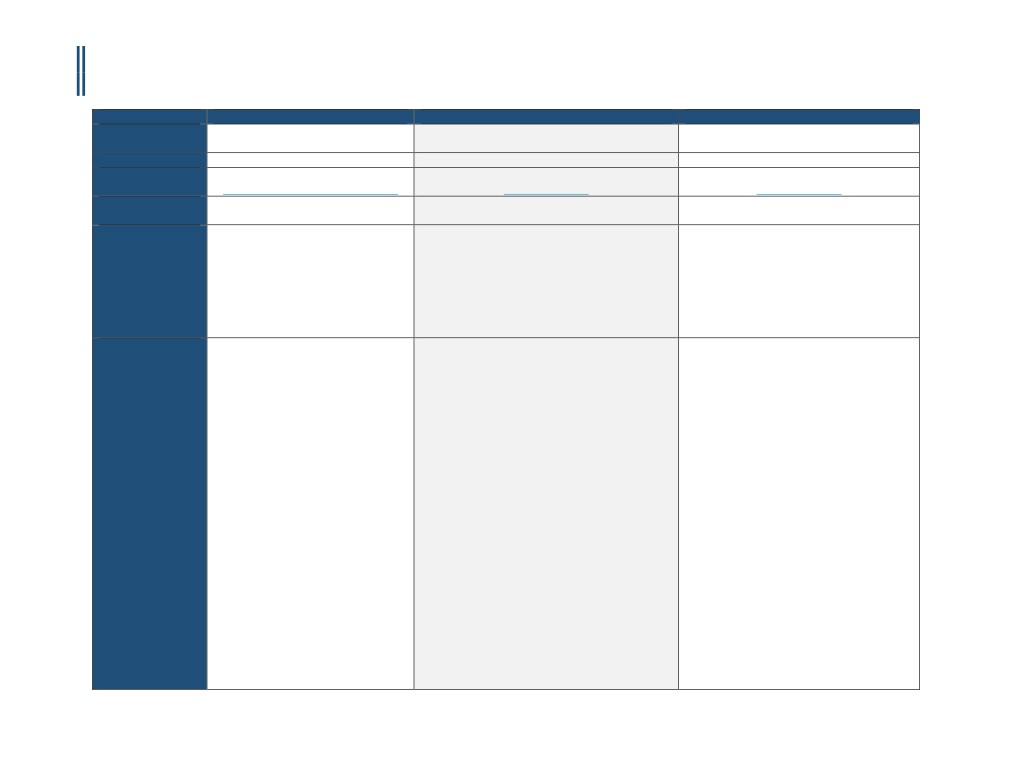
Payer
BlueCross BlueShield Illinois
Aetna
Cigna
Policy Name
Computed Tomography Angiography
Cardiac CT, Coronary CT Angiography and Calcium
Cigna Medical Coverage Policies - Radiology
(CTA)
Scoring
Cardiac Imaging
Policy #
RAD604.007
0228
RBM
AIM Specialty Health® (AIM)
eviCore (Product line and POS dependent)
eviCore (Product line and POS dependent)
Applicable CPT
75574
75574
75574
Code(s)
Applicable ICD
Not Listed
E08.00 - E09.9
Not Listed
Code(s)
E10.10 - E13.9
Not all-inclusive
I37.0 - I37.9
M30.3
Q21.3
Q26.0 - Q26.9
Q87.40 - Q87.43
R94.39
Covered
• Contrast-enhanced computed
I. Aetna considers cardiac computed tomography
1. For symptomatic individuals who have a very
tomography (CT) angiography (CTA) for
(CT) angiography of the coronary arteries using 64-
low, low, or intermediate pretest probability
evaluation of patients without known
slice or greater medically necessary for the
of CAD, CCTA may be used in the following
coronary artery disease (CAD) who
following indications:
situations:
present with acute chest pain in the
a. Unable to perform either an exercise or
emergency room or emergency
A.
Rule out significant coronary stenosis in
pharmacologic imaging stress test
department setting may be considered
persons with a low or intermediate pre-test
b.Stress test (treadmill or imaging stress
medically necessary.
probability of coronary artery disease or
test) is uninterpretable, equivocal, or a
atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease by
false positive is suspected
• Contrast-enhanced CTA for evaluation
Framingham risk scoring, Pooled Cohort
c. Replace performance of invasive coronary
of patients with suspected ischemic
Equations, or by American College of Cardiology
angiogram
heart disease, who meet guideline
(ACC) criteria (see Appendix), with any of the
2. For symptomatic individuals, evaluate post-
criteria for a noninvasive test in the
following indications:
CABG graft patency when only graft patency is
outpatient setting may be considered
1. Evaluation of persons with chest pain who
a concern and imaging of the native coronary
medically necessary (refer to NOTE
cannot perform or have contraindications to
artery anatomy is not needed, such as in early
1 below).
exercise and pharmacological stress testing; or
graft failure.
2. Evaluation of persons with chest pain
3. For symptomatic individuals with
NOTE 1: A noninvasive test should be
presenting to the emergency department in
unsuccessful conventional coronary
performed on patients with at least
persons without acute ECG changes or positive
angiography.
intermediate risk for coronary artery
coronary markers when an imaging stress test
4. Re-do CABG: To identify whether bypass
disease (10%-90% risk by standard risk
or coronary angiography are being deferred as
grafts are located directly beneath the
prediction instruments/pre-test
the initial imaging study.
sternum, so that alternative ways to enter the
probability assessments). The choice of
chest can be planned.
test will depend on:
B.
Rule out significant coronary stenosis in
persons with a low pre-test probability of coronary
1
CCM-100-101-A
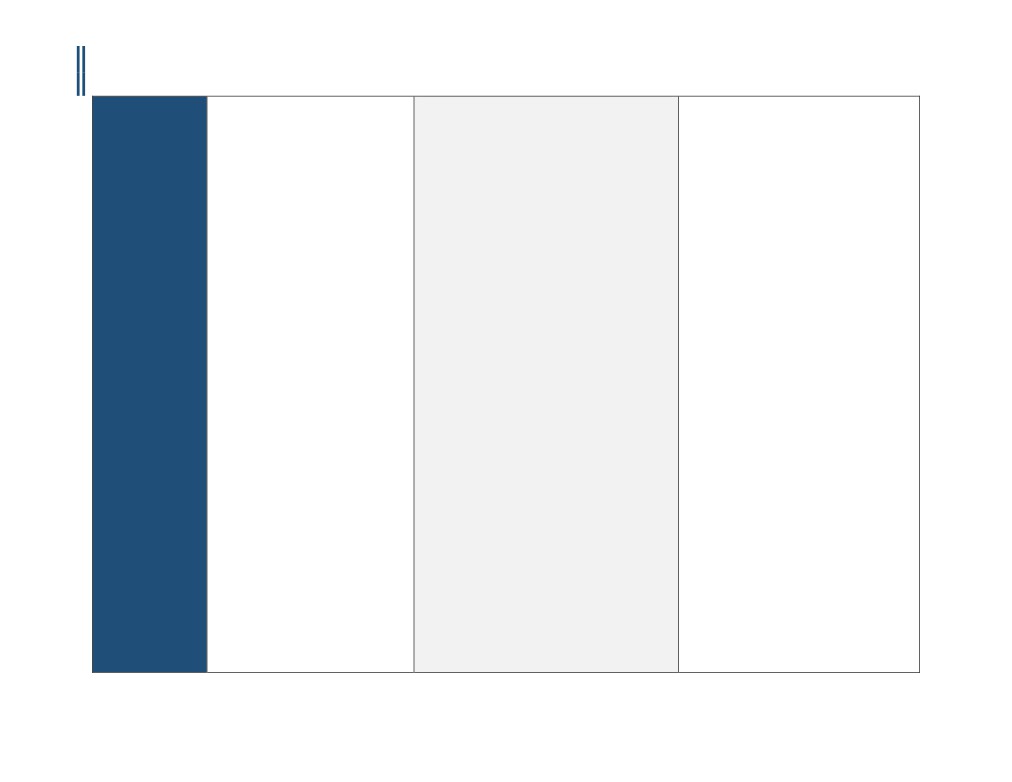
ILLINOIS - CORONARY CTA PRIOR-AUTHORIZATION INFORMATIONAL GUIDE
Updated October 6th, 2016
1.
Interpretability of the
artery disease or atherosclerotic cardiovascular
5. Evaluate coronary artery anomalies and other
electrocardiogram;
disease by Framingham risk scoring, Pooled Cohort
complex congenital heart disease of cardiac
2.
Ability to exercise; and
Equations, or by American College of Cardiology
chambers or great vessels
3.
Presence of comorbidities
(ACC) criteria (see Appendix) with a positive (i.e.,
6. Anomalous coronary artery(ies) suspected for
greater than or equal to 1 mm ST segment
diagnosis or to plan treatment and less than
• Contrast-enhanced CTA for evaluation
depression) stress test.
age 40 with a history that includes one or
of anomalous (native) coronary
more of the following
arteries in patients in whom they are
C.
Evaluation of asymptomatic persons at an
a. Persistent exertional chest pain and
suspected may be considered
intermediate pre-test probability of coronary heart
normal stress test
medically necessary when
disease or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease by
b.Full sibling(s) with history of sudden death
conventional angiography is
Framingham risk scoring or Pooled Cohort
syndrome before age 30 or with
unsuccessful or equivocal and when
Equations (see Appendix) who have an equivocal or
documented anomalous coronary artery
the results will impact treatment
uninterpretable exercise or pharmacological stress
c. Resuscitated sudden death and
test.
contraindications for conventional
coronary angiography
D.
Pre-operative assessment of persons
7. Unexplained new onset of heart failure
scheduled to undergo 'high-risk" non-cardiac surgery,
8. Evaluation of newly diagnosed congestive
where an imaging stress test or invasive coronary
heart failure or cardiomyopathy
angiography is being deferred unless absolutely
a. No prior history of coronary artery
necessary. The ACC defines high-risk surgery as
disease, the ejection fraction is less than
emergent operations, especially in the elderly, aortic
50 percent, and low or intermediate risk
and other major vascular surgeries, peripheral
on the pre-test probability assessment
vascular surgeries, and anticipated prolonged surgical
AND
procedures with large fluid shifts and/or blood loss
b.No exclusions to cardiac CT angiography
involving the abdomen and thorax.
c. No cardiac catheterization, SPECT, cardiac
PET, or stress echocardiogram has been
E.
Pre-operative assessment for planned non-
performed since the diagnosis of
coronary cardiac surgeries including valvular heart
congestive heart failure or
disease, congenital heart disease, and pericardial
cardiomyopathy
disease, in lieu of cardiac catheterization as the initial
9. Ventricular tachycardia (6 beat runs or
imaging study.
greater) if CCTA will replace conventional
invasive coronary angiography
F.
Detection and delineation of suspected
10. Equivocal coronary artery anatomy on
coronary anomalies in young persons (less than 30
conventional cardiac catheterization
years of age) with suggestive symptoms (e.g., angina,
11. Newly diagnosed dilated cardiomyopathy
syncope, arrhythmia, and exertional dyspnea without
12. Preoperative assessment of the coronary
other known etiology of these symptoms in children
arteries in patients who are going to undergo
and adults; dyspnea, tachypnea, wheezing, periods of
surgery for aortic dissection, aortic aneurysm,
pallor, irritability (episodic crying), diaphoresis, poor
or valvular surgery if CCTA will replace
feeding and failure to thrive in infants).
conventional invasive coronary angiography
13. Vasculitis/Takayasu‘s/Kawasaki‘s disease
2
CCM-100-101-A
ILLINOIS - CORONARY CTA PRIOR-AUTHORIZATION INFORMATIONAL GUIDE
Updated October 6th, 2016
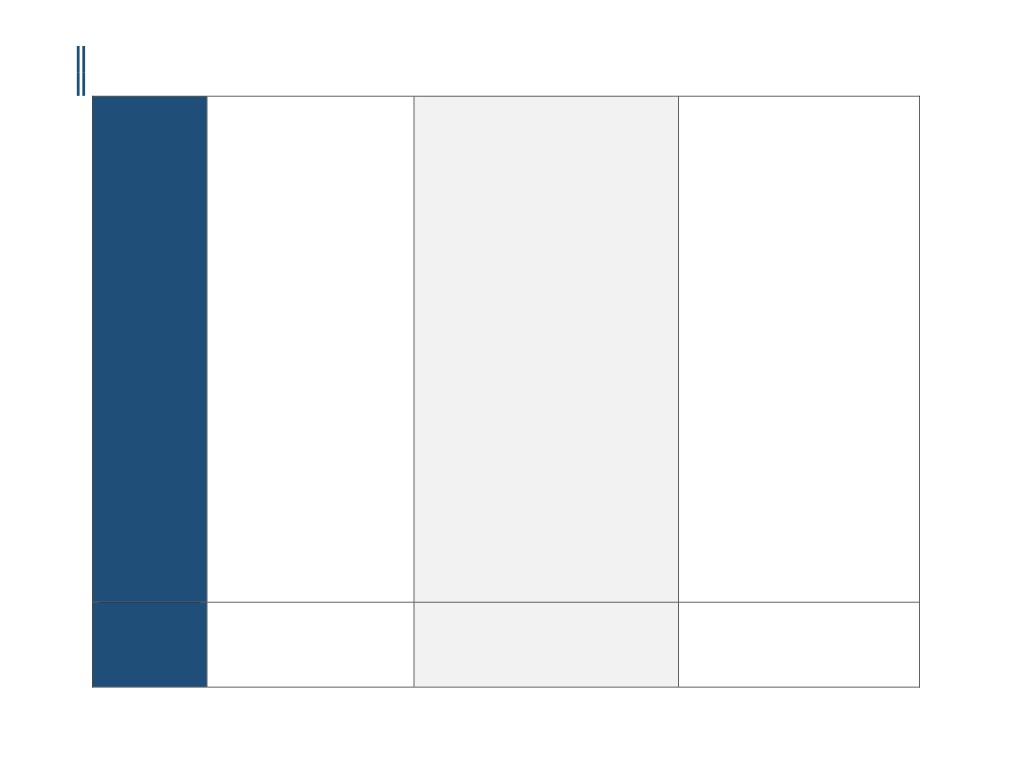
II. Aetna considers CT angiography of cardiac
morphology for pulmonary vein mapping medically
necessary for the following indications:
A.
Evaluation of persons needing biventricular
pacemakers to accurately identify the coronary veins
for lead placement.
B.
Evaluation of the pulmonary veins in
persons undergoing pulmonary vein isolation
procedures for atrial fibrillation (pre- and post-
ablation procedure).
III.
Aetna considers CT angiography medically
necessary for preoperative assessment of the
aortic valve annulus prior to
anticipated transcatheter aortic valve replacement
(TAVR).
IV.
Aetna considers cardiac CT for evaluating
cardiac structure and morphology medically
necessary for the following indications:
A. Anomalous pulmonary venous drainage;
B. Evaluation of other complex congenital
heart diseases;
C. Evaluation of sinus venosum atrial-septal
defect;
D. Kawasaki's disease;
E. Person scheduled or being evaluated for
surgical repair of tetralogy of Fallot or
other congenital heart diseases;
F.
Pulmonary outflow tract obstruction;
G.
Suspected or known Marfan's syndrome.
Not Covered /
• Contrast-enhanced CTA for coronary
1.Aetna considers cardiac CT angiography
1. Irregular heart rhythms (e.g., atrial
Investigational and
artery evaluation is considered
experimental and investigational for persons with
fibrillation/flutter, frequent irregular
Not Medically
experimental, investigational and/or
any of the following contraindications to the
premature ventricular contractions or
Necessary
unproven for all other indications,
procedure because its effectiveness for indications
premature atrial contractions, and high grade
including but not limited to:
other than the ones listed above has not been
heart block)
established:
2. Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT)
3
CCM-100-101-A
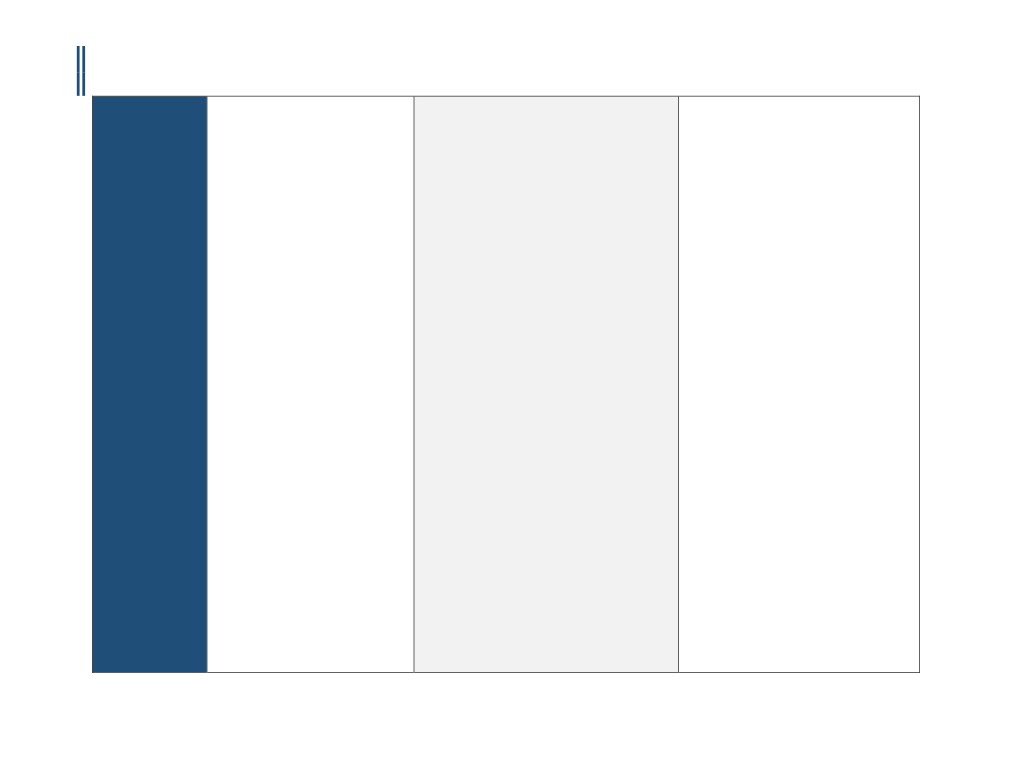
ILLINOIS - CORONARY CTA PRIOR-AUTHORIZATION INFORMATIONAL GUIDE
Updated October 6th, 2016
o Screen asymptomatic individuals
3. Inability to lie flat
for CAD; OR
A. Body mass index (BMI) greater than 40.
4. Body mass index of 40 or more
o Evaluate individuals with cardiac
B. Inability to image at desired heart rate (under
5. Inability to obtain a heart rate less than 65
risk factors in lieu of cardiac
80 beats/min), despite beta blocker
beats per minute after beta-blockers
evaluation and standard non-
administration.
6. Calcium (Agatston) score of 1000 or more
invasive cardiac testing; OR
C. Person with allergy or intolerance to iodinated
7. Inability to hold breath for at least 8 seconds
o Evaluate individuals for any other
contrast material
8. Renal Insufficiency
indication not listed above,
D. Persons in atrial fibrillation or with other
9. Asymptomatic patients and routine use in the
including but not limited to high
significant arrhythmia.
evaluation of the coronary arteries following
or low pretest probability (low
E. Persons with extensive coronary calcification
heart transplantation
risk defined as <10% and high risk
by plain film or with prior Angston score
10. Evaluation of coronary stent patency (metal
as >90%) of CAD.
greater than 1,700.
artifact limits accuracy)
11. Evaluation of left ventricular function
• Coronary CTA performed using a multi-
2. Aetna considers cardiac CT angiography using less
following myocardial infarction or in chronic
detector row computed tomography
than 64-slice scanners experimental and
heart failure
scanner with less than 64-slice scanner
investigational because the effectiveness of this
12. Evaluation of patients with postoperative
is considered experimental,
approach has not been established.
native or prosthetic cardiac valves who have
investigational and/or unproven.
technically limited echocardiograms, MRI or
3.Aetna considers coronary CT angiography
TEE.
• The use of noninvasive fractional flow
experimental and investigational for screening of
13. First test in evaluating symptomatic patients
reserve (FFR) CT simulation to evaluate
asymptomatic persons, evaluation
(e.g. chest pain)
and assess coronary blood flow
of atherosclerotic burden, evaluation of persons at
14. Irregular heart rhythms (e.g., atrial
quantity and velocity for any cardiac
high pre-test probability of coronary artery disease,
fibrillation/flutter, frequent irregular
condition, with or without a prior
evaluation of stent occlusion or in-stent restenosis,
premature ventricular contractions or
coronary CTA, is considered
evaluation of persons with an equivocal PET
premature atrial contractions, and high grade
experimental, investigational and/or
rubidium study, identification of vulnerable
heart block)
unproven.
plaques, monitoring of atheroma burden, and for
15. High pre-test probability for CAD—rather,
all other indications (e.g., atrial
these patients should undergo conventional
angiosarcoma) because its effectiveness for these
coronary angiography, especially if an
indications has not been established.
interventional procedure (e.g., PCI) is
anticipated
16. Identification of plaque composition and
morphology
17. Myocardial perfusion and viability studies
18. Preoperative assessment for non-cardiac,
nonvascular surgery
19. Repeat or routine follow-up of CAD with
CCTA
20. There is insufficient evidence to support
routine use of Coronary Computed
Tomography Angiography (CCTA) in the
4
CCM-100-101-A

ILLINOIS - CORONARY CTA PRIOR-AUTHORIZATION INFORMATIONAL GUIDE
Updated October 6th, 2016
evaluation of the coronary arteries following
heart transplantation.
Payer Specific
Requirements
Effective Date
8/15/2016
4/15/2016
5/12/2016
Last Review/
2/15/2007
4/9/1998
2/19/2016
Original Policy Date
SUGGESTED DOCUMENTATION TO NAVIGATE PRE-AUTHORIZATION
For instances when the indication is medically necessary, clinical evidence is required to determine medical necessity. For instances when the indication is investigational, you
may submit additional information to the Prior Authorization Department. The following documentation is recommended in order to ensure that pre-authorization can be
secured in a timely and efficient manner:
1.
Medical chart notes - all notes from the patient chart related to the requested procedure, including patient’s current cardiac status/ symptoms, cardiac
factors, and indications.
2.
Relevant patient information, including:
▪ Patient age, height, weight, and BMI
▪ Family history of heart problems (including relationship to member, age at diagnosis, type of event, etc.)
▪ Medical history (e.g. diabetes, hypertension, stroke arrhythmia, etc.)
▪ Cardiac risk factors
▪ Previous cardiac treatments, surgeries, or interventions
▪ Problems with exercise capacity
▪ Ordering provider information
▪ Imaging provider information
▪ Imaging exam(s) being requested (body part, right, left, or bilateral)
▪ Patient diagnosis (suspected or confirmed)
3.
Diagnostic or imaging reports from previous tests (exercise stress test, echocardiography, stress echocardiography, MPI, coronary angiography, etc.)
4.
Symptom history (onset, course, new or changing symptoms) related to all pertinent cardiac conditions, such as heart muscle/ valvular disease, structural
abnormality, infection, exposure to toxins/ chemotherapy, etc.
5.
Examination results, including evaluation of hypertension, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, abnormal rhythm, pulmonary embolus, congenital condition, etc.
6.
Any other documentation that supports the need for the procedure
DISCLAIMER: The information provided in this document is general information only and is not provided as legal advice, nor is it advice about how to code, complete, or submit any particular claim for
payment for health care services or goods. This information provides only an overview of HeartFlow’s understanding of current coverage policies for a select number of payers, and may not provide
all the information necessary to understand a particular patient’s benefits or payers coverage policies and prior authorization requirements. The information provided may not be comprehensive or
complete. It is the responsibility of the health care provider, such as a hospital or a physician to verify coverage and prior authorization requirements, submit complete, accurate and appropriate bills
or claims for payment that comply with applicable laws and regulations and third-party payer requirements, and to determine the appropriate codes, charges, and modifiers that the provider uses for
those purposes. Third-party payers may have policies and coding requirements that differ from those described here, and such policies can change over time.
HeartFlow disclaims any responsibility for claims submitted by health care physicians or others. Physicians should check and verify current policies and requirements with the payer for each patient.
HeartFlow endorses the best practice that all coding and billing submissions to payers be truthful and not misleading, and that providers make full disclosures to the payer about how the service has
been used. HeartFlow cannot guarantee success in obtaining payment for products and services.
5
CCM-100-101-A

ILLINOIS - CORONARY CTA PRIOR-AUTHORIZATION INFORMATIONAL GUIDE
Updated October 6th, 2016
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) copyright 2016.
All rights reserved. CPT® is a registered trademark of the American Medical Association (AMA). Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by
the AMA, are not part of CPT coding, and the AMA is not recommending their use.
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10) is maintained by the National Center for Health Statistics and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid
Services.
References:
1.
“Cardiac Checklist (Health Plan).” RadMD, http://www1.radmd.com/media/459739/template-cardiac-checklist-magellan-hc-logo-4-1-2016.pdf. Accessed 25 October 2016.
2.
“AIM Specialty Health (AIM) Ordering Physician/Provider Quick Tips for Diagnostic Imaging Management Programs.” Anthem,
https://www11.anthem.com/provider/nh/f5/s2/t0/pw_ad087257.pdf. Accessed 25 October 2016.
6
CCM-100-101-A